Tungsten Copper Rod Hardness
Introduction
The capacity of resisting a hard object pressed into its surface is called as hardness in physics. And tungsten copper rod hardness is the basic indicator to evaluate the materials if soft or hard.
Types
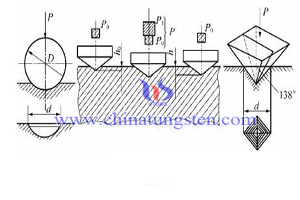
Tungsten copper hardness can be divided into scratch hardness, indentation hardness and rebound hardness. Scratch hardness: Mainly used to compare the hardness of minerals, the method is selected from the soft end of a hard rod end, it will be measured along the rod across the material, soft and hard material being tested is determined according to the position of scratches (the hard draws a long scratch and the soft draws a short scratch); Indentation hardness: Mainly used for metal materials, the method is to use a certain predetermined load of indenter into the test material, soft and hard surface of the material to local plastic deformation of the material being tested to compare the size (according to different indenter, load and duration, it also can be specifically divided into Brinell hardness, Rockwell hardness, Vickers hardness and micro hardness and so on); Rebound hardness: Mainly used for metal materials, the method is to make a special free-fall from a certain height hammer impact test material, and specimen storage during impact (and then release) the strain energy of the number (by hammers bouncing height measurement) to determine material hardness.

Conversion
Common types of tungsten copper alloy hardness: Brinell hardness (HB) or Rockwell hardness (HRR). 1. Shore hardness (HS) = Brinell hardness (BHN) / 10 + 12; 2. Shore hardness (HS) = Rockwell hardness (HRC) +15; 3. Brinell hardness (BHN) = Locke hardness (HV); 4. Rockwell hardness (HRC) = Brinell hardness (BHN) / 10-3.
Any feedback or inquiry of Tungsten Copper Alloy Products please feel free to contact us:
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tel.: +86 592 512 9696 ; +86 592 512 9595
